Introduction: The Battle of the Birds – Mockingbird vs Blue Jay
Have you ever spotted a bird in your backyard and wondered what it is? If you’ve been lucky enough to observe a mockingbird and a blue jay in action, you may have noticed how similar yet different these two birds can be. While both are common in North America and share a penchant for being quite vocal, they each possess unique traits that set them apart. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between the mockingbird vs blue jay, including their physical features, behavior, and habitat preferences, helping you easily identify them in the wild.
Physical Characteristics: How to Spot the Difference
Mockingbird Physical Traits
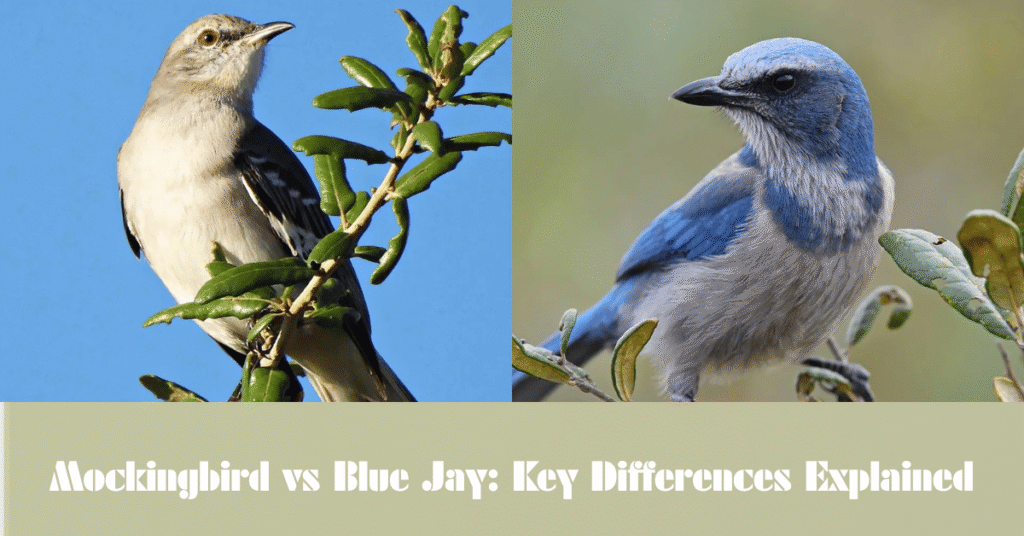
The northern mockingbird is a medium-sized bird with a slender body and long tail. Its feathers are mostly grayish-brown with subtle streaks across its chest and belly, making it a bit more muted in appearance compared to other birds. The most striking feature is its long tail, which is often fanned out as the bird perches or flies.
Mockingbirds have white wing patches that become visible during flight, and their eyes are bright and keen, always on the lookout. Despite their somewhat dull-colored plumage, mockingbirds are known for their agility and quick flight patterns.
Blue Jay Physical Traits
In contrast, the blue jay is an eye-catching bird, famous for its vibrant blue feathers, striking black markings around its neck, and white undersides. Its feathers shimmer in shades of blue, which can range from light to dark, depending on the angle of the light. The blue jay also has a prominent crest on its head, which adds to its dramatic appearance.
Not as long-tailed as the mockingbird, the blue jay has a more compact, rounded shape. The bird’s beak is slightly stronger, and it has a distinctive white and black pattern on its face, making it easy to spot from a distance.
Behavior and Personality: The Mockingbird’s Mimicry vs The Blue Jay’s Boldness
Mockingbird: A Master Mimic
One of the most fascinating aspects of the mockingbird’s behavior is its incredible mimicry skills. A single mockingbird can mimic the songs of up to 200 different bird species, as well as other sounds like car alarms, dogs barking, and even phone ringtones. This mimicry is not just for show; it plays a role in attracting mates and defending territory.
Mockingbirds are known for being territorial and can become aggressive if they feel their space is threatened, especially during the breeding season. They have a unique flight pattern, hopping from perch to perch while emitting various calls and songs. These birds are often seen perched atop trees or fences, singing loudly to assert their presence.
Blue Jay: Bold and Social
On the other hand, blue jays are much more social and bold in their interactions. While they do not have the same mimicking abilities as mockingbirds, blue jays are known for their loud, sharp calls and distinct “jay” sound. These birds are highly intelligent and are capable of using tools, solving complex problems, and even mimicking human speech, though not to the extent of mockingbirds.
Blue jays are known for their boldness in foraging. They often forage in groups and are not shy about stealing food from other birds or animals. They also have a complex social structure, often seen in family groups or flocks during the colder months. Unlike mockingbirds, blue jays can be aggressive when defending food or territory, often intimidating smaller birds.
Habitat Preferences: Where to Find These Birds
Mockingbird Habitat
Mockingbirds are found in a variety of habitats, from suburban neighborhoods to open fields and deserts. These adaptable birds prefer open areas with scattered shrubs or trees that provide perching spots and opportunities for foraging. They thrive in areas with plenty of open ground where they can easily search for insects, fruits, and seeds.
In the southern United States, mockingbirds are especially prevalent. They are often spotted in parks, gardens, and backyards, as long as there’s some kind of structure to support their territorial singing.
Blue Jay Habitat
Blue jays, on the other hand, prefer wooded areas, especially in areas with oak, pine, and beech trees. They are often found in both urban and rural environments but are most commonly associated with forests and woodland edges. These birds are highly adaptable but prefer the safety of trees for nesting and roosting.
While they are common across North America, blue jays are particularly prevalent in the eastern and central regions of the United States, although their range extends to parts of Canada as well. They are known to be year-round residents in many areas, where they form large, social groups during the winter months.
Diet: What Mockingbirds and Blue Jays Eat
Mockingbird Diet
Mockingbirds are omnivorous and have a varied diet that includes insects, fruits, seeds, and small reptiles. They are especially fond of berries, and their diet can change depending on the season. During the summer, they may focus on insects like grasshoppers, while in the winter, they might turn to berries and seeds to sustain them.
These birds are excellent foragers and will often hunt on the ground or in low shrubs. Their diet also includes small lizards, which they catch with their quick reflexes.
Blue Jay Diet
Blue jays are also omnivores but tend to favor a diet rich in acorns, seeds, nuts, and fruits. They are notorious for raiding bird feeders and stealing food from other animals. While they will eat insects and small animals on occasion, their primary diet revolves around seeds and nuts, especially during the fall and winter when food is scarce.
Interestingly, blue jays play a crucial role in the dispersal of acorns, which they often bury to eat later. Some of these acorns may germinate and grow into new oak trees, making blue jays an important part of forest ecosystems.
Lifespan and Reproduction: Starting a Family
Mockingbird Lifespan
In the wild, mockingbirds typically live for about 3-4 years, although some may survive longer if they manage to avoid predators and environmental hazards. They breed in the spring and summer, often having multiple broods per year. The female will build a cup-shaped nest in a shrub or tree, and both parents help to care for the young.
Blue Jay Lifespan
Blue jays have a similar lifespan, living on average 7 years in the wild, though they can sometimes live up to 15 years if they avoid predators. They are monogamous, with pairs typically staying together for life. Blue jays build their nests high in trees, usually in dense foliage to avoid detection by predators. Both parents are involved in raising the young, feeding them a diet of insects, seeds, and berries.
Mockingbird vs Blue Jay: Which One is Right for Your Backyard?
If you’re deciding whether to attract a mockingbird or blue jay to your backyard, consider what each bird can offer:
-
Mockingbirds: Perfect if you enjoy the sound of constant song and appreciate a bird that can mimic other creatures. They’re ideal for open spaces and can add variety with their diverse calls.
-
Blue Jays: Choose blue jays if you want a more social bird that’s vibrant in both appearance and behavior. They’re bold, intelligent, and a bit more showy, making them a fascinating addition to any garden or woodland area.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do mockingbirds and blue jays get along?
Mockingbirds and blue jays can sometimes compete for territory and food. However, they often occupy different niches within the ecosystem, with mockingbirds preferring more open spaces and blue jays favoring wooded areas.
2. Are blue jays and mockingbirds good for birdwatching?
Both birds are excellent for birdwatching. Mockingbirds are highly vocal and active, offering plenty of entertainment with their songs. Blue jays, on the other hand, are strikingly beautiful and exhibit fascinating behaviors like tool use and complex social structures.
3. Can I attract both mockingbirds and blue jays to my backyard?
Yes, with the right setup, it’s possible to attract both birds. Make sure you provide a mix of open spaces for mockingbirds and trees or shrubs for blue jays to nest in.
Conclusion: The Uniqueness of Mockingbirds and Blue Jays
When it comes to choosing between a mockingbird vs blue jay, it all comes down to what you’re looking for in a backyard bird. Mockingbirds bring a musical touch with their incredible mimicry skills, while blue jays captivate with their striking appearance and social behaviors. Whether you’re fascinated by their songs or intrigued by their intelligence, both birds have their unique charm. Next time you spot one of these feathered friends, you’ll be able to appreciate the subtle differences that make them so special!